Zigbee and it’s architecture
- Jul 27, 2019
- by Spikebot
Zigbee and it’s architecture
What is Zigbee
Zigbee is an energy-efficient and cost-efficient wireless network standard. It utilizes mesh network topology, permitting it gives high unwavering quality and a sensible range.
One of Zigbee’s highlight is its ability to provide secure communication. This is practiced using 128-bit cryptographic keys. This framework depends on symmetric keys, which implies that both the beneficiary and originator of exchange need to have a similar key. These keys are either pre-introduced, shipped by a “trust focus” assigned inside the network or set up between the trust focus and a device without being moved.
Zigbee operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 particular and is utilized to make networks that require a low data transfer rate, secure networking, and energy efficiency. It is utilized in various applications, for example, building automation frameworks, climate control, and medical devices. ZigBee is designed in such a way that is more affordable and simple as compared to other PAN (Personal Area Network) technologies like Bluetooth.
Zigbee supports diverse network configurations for the master to master or master to slave communications. And furthermore, it tends to be operated in various modes, therefore, the battery power is moderated. Zigbee networks are extendable with the utilization of routers and enable numerous hubs to interconnect with one another for a more extensive territory network.
Zigbee Architecture
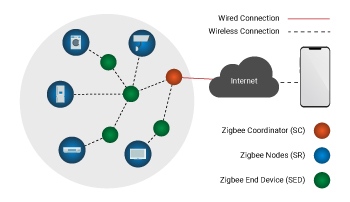
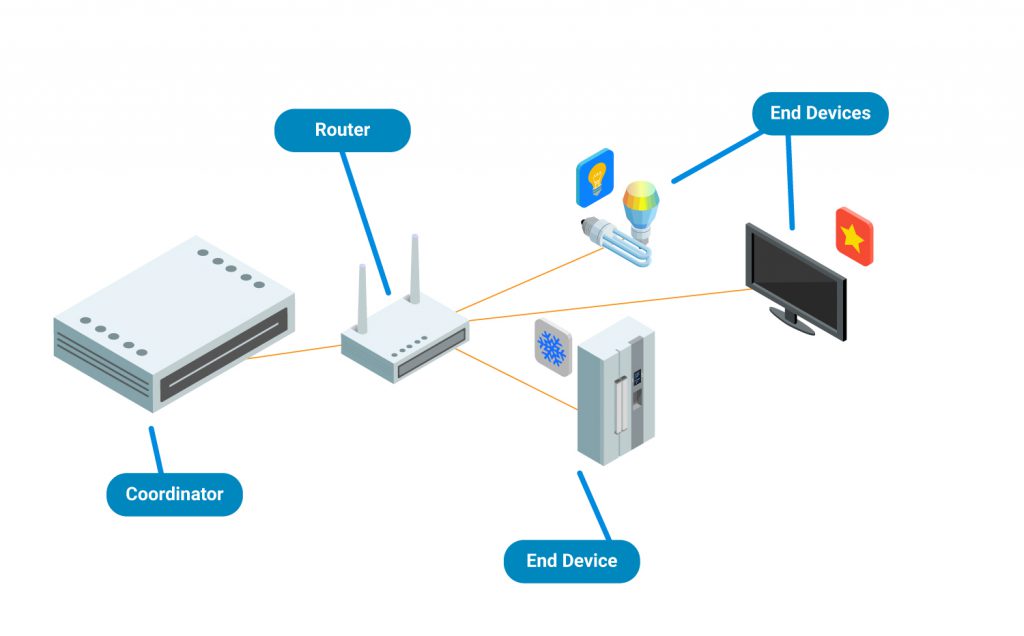
Zigbee framework structure comprises of three distinct kinds of devices, for example, Zigbee Coordinator, Router and End device. Every Zigbee network consists of one coordinator at least. This coordinator acts as a root and bridge of the network. The organizer is in charge of dealing with and putting away the data while performing receiving and transmitting data information. Zigbee routers act as intermediary devices. They are responsible for permitting data to transfer between them and other devices. As a result battery power is saved as end devices have limited functionality to communicate with the nodes. Also depending on the type of networks such as a star, mesh or tree we decide the number of routers, coordinators and end devices.
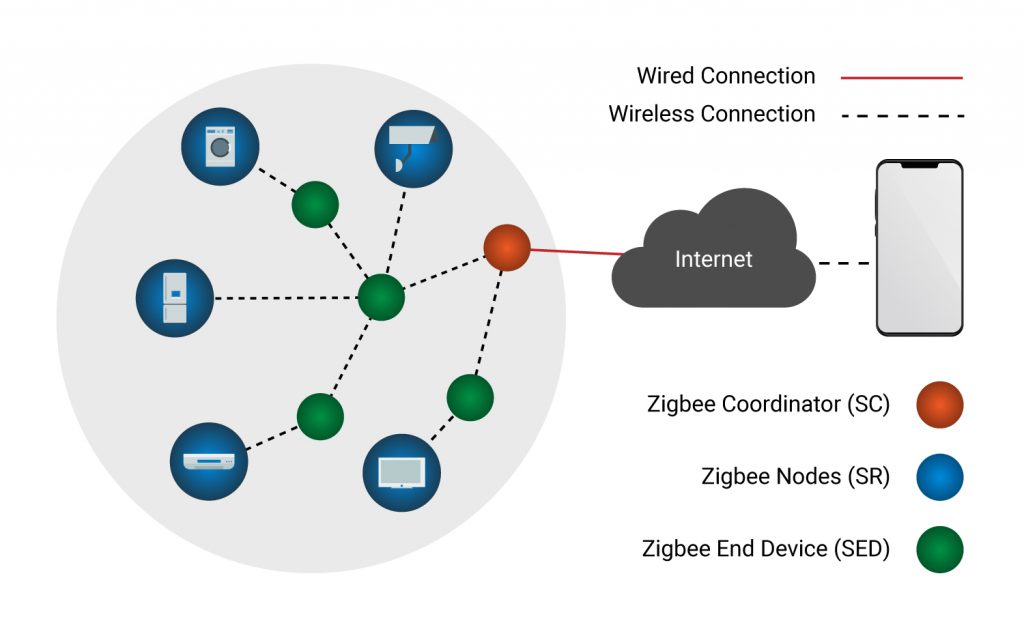
Zigbee protocol architecture comprises of a pile of different layers where IEEE 802.15.4 is characterized by physical and MAC layers while this convention is finished by collecting Zigbee’s very own system and application layers.
Physical Layer
This layer does regulation and demodulation activities after transmitting and accepting signals separately.
MAC Layer
This layer is in charge of the reliable transmission of information. This is done by accessing various systems with the carrier sense multiple access collision avoidances (CSMA). For synchronizing communication, this additionally transmits the beacon frames.
Network Layer
All the network-related operations such as end device connection, network setup and disconnection to routing, network, and device configuration, etc. are taken care of by the network layer.
Application Support Sub-Layer
This layer empowers the administrations essential for Zigbee device object and application objects to interface with the network layers for managing data. Application support sub-layer is responsible for matching the devices according to their needs and services.
Application Framework
Generic message services and Key value pair are the two types of data services provided, application framework. Key-value pair is used to attributes in the application objects while the generic message is the developer-defined structure. It is responsible for detecting, initiating and binding other devices to the network.
Zigbee Operating Modes and Its Topologies
Zigbee two-way data is moved in two modes: Non-beacon mode and Beacon mode. In a beacon mode, the routers and coordinators continuously monitor the active state of incoming data. This simply means that more power is consumed. In this mode, the routers and coordinators do not sleep. This is because any node can wake up at any time and start communicating. However, it requires more power supply and its overall power consumption is low because most of the devices are in an inactive state for over long periods in the network.
In a beacon mode, when there is no data communication from end devices, then the routers and coordinators enter into a sleep state. Periodically this coordinator wakes up and transmits the beacons to the routers in the network. These beacon networks are work for time slots which means, they operate when the communication needed results in lower duty cycles and longer battery usage. These beacon and non-beacon modes of Zigbee can manage periodic (sensors data), intermittent (Light switches) and repetitive data types.
Zigbee supports a few network topologies; be that as it may, the most generally utilized setups are the star, mesh and cluster tree topologies. Every topology comprises at least one coordinator.
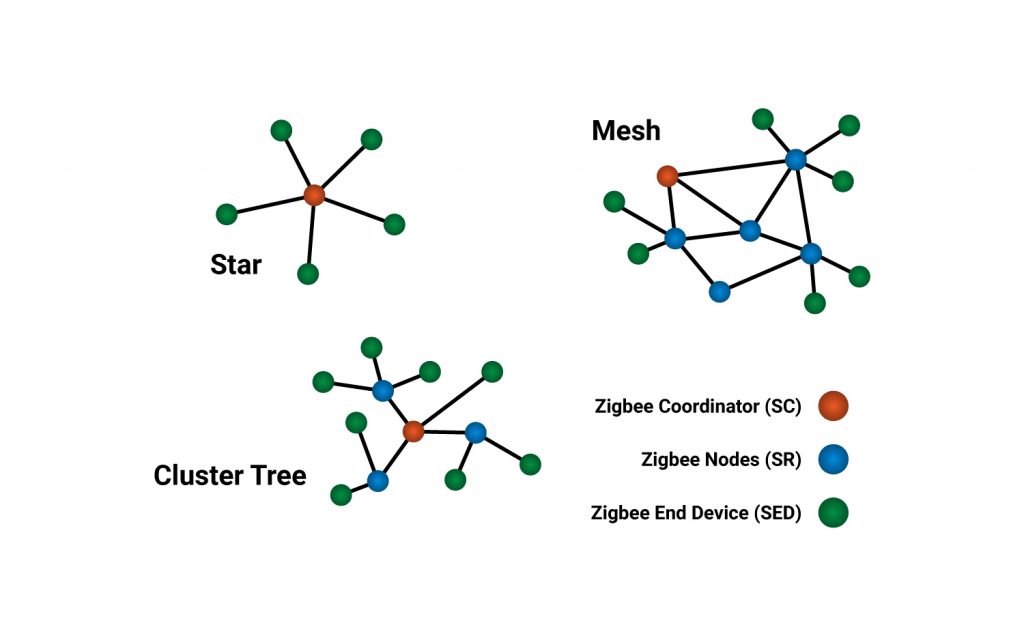
In a star topology, the network comprises of one coordinator that is responsible for starting and managing all the devices over the network. Every other device is called an end device. End device directly communicates with the coordinator. Star topology is simple and easy to deploy. Star topology is used in industries where they need all the end devices to communicate to the central controller.
In mesh and tree topologies, the Zigbee network is extended with a few routers where the coordinator is responsible for initiating. Mesh and Tree topologies allow devices to communicate with other adjacent nodes. This is done to provide redundancy of data. In case a node fails, information is routed automatically by these topologies to other devices. Mesh topology is mostly used in the industries as redundancy is the major factor in them.
In a cluster tree network, each cluster consists of one coordinator along with leaf nodes. These coordinators are connected to the parent coordinator which initiates the entire network.
